Fears of ‘false start’ for Fed leave emerging markets in limbo
[ad_1]
Since the Fed kicked off its long-anticipated loosening cycle on September 18 with a cut of 50 basis points, double the median forecast, emerging-market assets have traded as if borrowing costs in the world’s largest economy will remain high. That’s left developing world assets in limbo, headed for another span of underperformance.
In little over a month, the Fed rate cut has been eclipsed by fresh risks that are keeping global investors shy on the asset class, overshadowing the gains that Fed easing cycles might usually be expected to bring. While the threats have taken different forms — higher Treasury yields, a stronger dollar, greater volatility in currency options — the underlying themes have been just two: The potential return of Donald Trump as US president and China’s inadequate stimulus measures.
That means that once again, traders in emerging markets are positioning defensively for an inflationary US economy and a deflationary Chinese one.
“We remain in a world with two potentially existential threats to EM – China weakness and Trump,” said Paul McNamara, investment director at Gam UK Ltd in London. “A strong US economy without inflation is good for EM, but persistent inflation will not only postpone further cuts, but weigh on all risk assets into the medium term.”
Though there was an initial boost to emerging markets from the Fed move, it was first interrupted by strong US data that revived fears of resurgent inflation, and later comments by presidential candidate Trump that exacerbated them. The Republican nominee has put tariffs and protectionism at the centre of his agenda. If implemented, that’s likely to raise consumer prices in the US and undermine demand for exports from the developing world, according to many economists.
“We’re just weeks away from a US election that might lead to a Trump economic assault on the biggest EM out there, China,” said Charlie Robertson, head of macro strategy at FIM Partners. “It’s close to a coin flip as to who wins the US election, and equally makes it hard to choose a local markets trade to like.”
Hedge funds have also been ramping up positions speculating on dollar gains against developing economies vulnerable to higher tariffs.
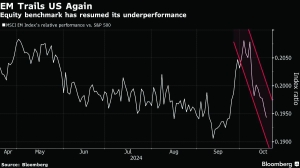
EM stocks, which briefly rebounded from a record low relative to US equities after the Fed decision, are heading back to that dubious honour. Local currencies and local-currency bonds are on course for their worst month since February 2023. Segments of the dollar-bond market, like long-duration and investment-grade, also continue to trail.
Bond investors have seen their returns stagnate in the month since the Fed decision. Their expectations for the developing world to follow the Fed are now being upended by central-bank caution, as policymakers from Indonesia to Hungary and Turkey decide to pause interest-rate cuts.
“Eventually EM local-currency bonds should benefit from global easing,” said Anders Faergemann, a senior portfolio manager at Pinebridge Investments. “However, from a total return perspective, the relief rally in the US dollar and domestic delays to monetary-policy easing may have triggered some profit-taking.”
The average yield on EM sovereign dollar bonds has edged higher by 9 basis points since September 18, while the rate on local-currency bonds has also risen 9 basis points, according to data compiled by Bloomberg. Between the two groups, the latter is underperforming in dollar returns, with currency declines acting as an additional drag.
“Rising geopolitical tensions, uncertainty over China’s efforts to rescue domestic consumption, and event risk leading up to the US presidential election will also spark increased demands for a higher risk premium into year end,” Faergemann said.
Strong US economic data have not only disrupted Fed monetary-policy bets but are also reshaping emerging-market yield curves. Within the dollar-bond market, investors are favouring short-duration bonds to long-duration bonds — an unlikely preference in an environment where falling rates are a consensus expectation. Bonds with a duration of more than 10 years have handed investors a loss of 3.6% since the Fed cut, while those of less than three years have given marginal gains.
As of Friday, swap traders were pencilling in further reductions to their bets on Fed cuts in the remaining two meetings of the year. Citigroup’s Akshay Singal, global head of short-term interest-rate trading, told Bloomberg TV that the Fed is likely to cut rates by just 25 basis points, or even stay put, over the next few meetings. He said he doubted the Fed would have opted for a 50-basis-point cut in September if it had seen the strong jobs data before the meeting.
“The combination of US Treasury yields above 4% and a pickup in economic activity in the US have called into question the idea of the beginning of a Fed cutting cycle,” said Martin Bercetche, a hedge-fund manager at UK-based Frontier Road Ltd. “We might have had a false start last month.”
For emerging-market stocks, the turbulence coming from the US economic and political landscape was just one of the problems. The wildest volatility in nine years has meanwhile gripped China as successive stimulus measures initially sparked a sharp equity rally, then ultimately failed to convince investors that they were enough to turn around the economy.
The EM equity benchmark, where China holds the biggest weighting, is once again trailing the S&P 500 Index, belying expectations that it would pull itself out of a seventh successive year of underperformance when the Fed started to cut rates.
The bruises of the past month have forced investors to reassess their exposure, and many are avoiding the sweeping EM-wide bets they’d recommended for the post-Fed era.
For the moment, the focus is on weathering the US election. With polls showing Trump is neck-and-neck with his Democratic rival Kamala Harris, a firmer view on EM has to wait. For Gam’s McNamara, there’s one scenario where the Fed-cut trades in emerging markets can begin to make money.
[ad_2]
Source link



