What is causing the haze blanketing Southeast Asia?

[ad_1]
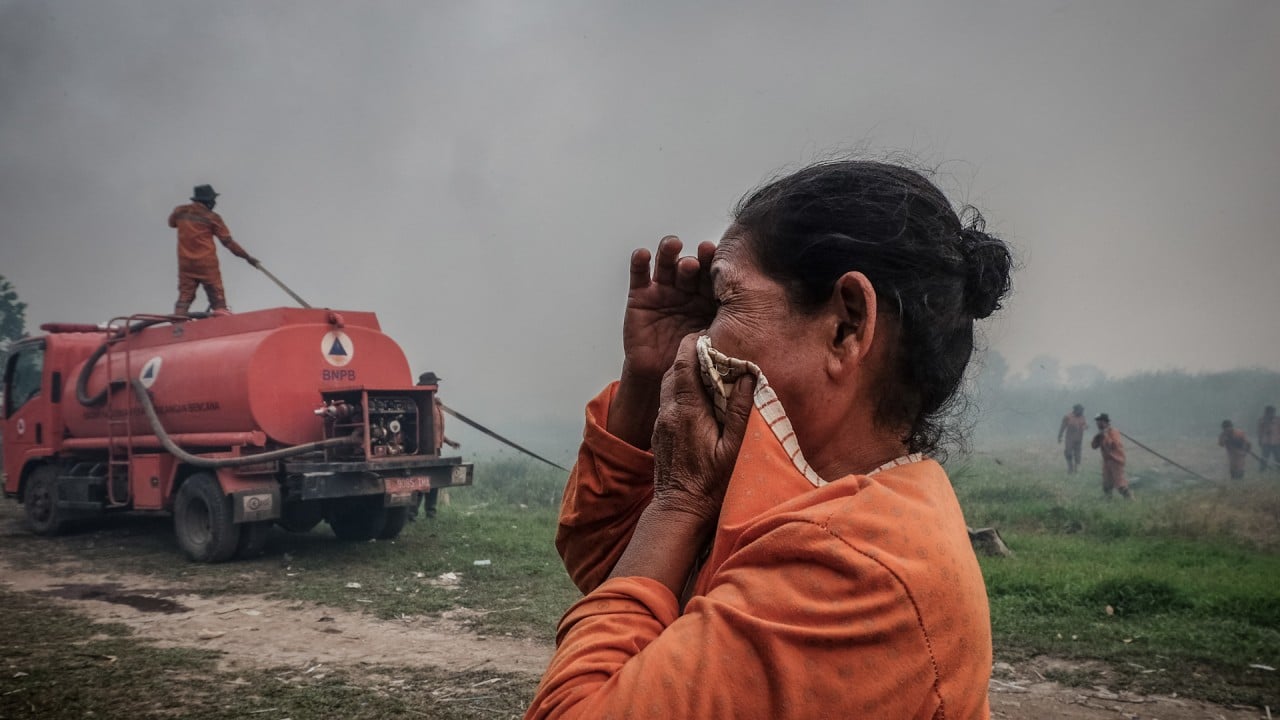
Every few years, during the dry season, smoke from “slash-and-burn” land clearing, largely to make way for oil palm, pulp and paper plantations, engulfs much of the region, posing a threat to public health, education and businesses such as tourism.
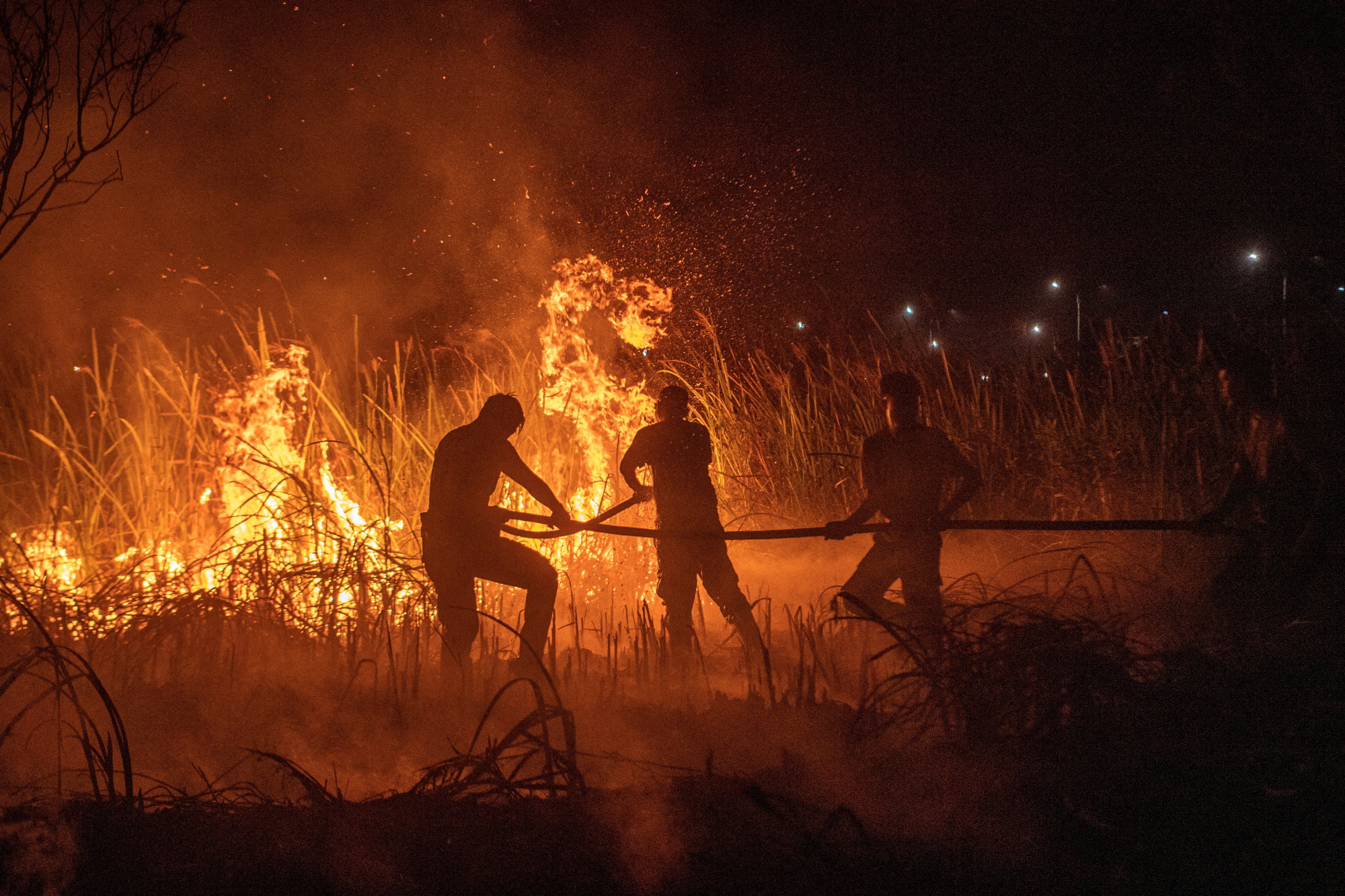
What’s being done about it?
Despite pleas by Malaysia last week not to “normalise” the haze, Indonesia has flatly denied any responsibility.
Indonesia’s Environment Minister Siti Nurbaya Bakar said on Friday that forest fires had declined and no haze was detected moving toward any neighbouring country.
Indonesia has been addressing the fires by water bombing via helicopters, she said.
Indonesia has in the past taken legal action against companies suspected of illegal burning, but each year fires continue with varying degrees of severity.
In 2015 and 2019 Indonesia was struck by catastrophic blazes that burned millions of hectares of land, causing record-breaking emissions and engulfing some places in toxic yellow smoke.
Why does this keep happening?
Under Indonesian law burning by small-scale local farmers is permitted provided it occurs on a maximum area of two hectares (five acres) and necessary prevention measures are in place.
All large-scale planters are obliged to comply with sustainable palm oil standards, which prohibit burning.
The regulations mean that slash-and-burn techniques continue to be used by smallholder farmers who rely on the cheap land-clearance method and for whom compliance to the standards is voluntary.
Southeast Asia haze crisis sparks fresh blame game, calls to deter ‘bad apples’
Southeast Asia haze crisis sparks fresh blame game, calls to deter ‘bad apples’
Intended to help members prevent, mitigate and monitor transboundary haze, the centre is in line with Asean’s commitment to achieve a haze-free region by 2030.
Asean agriculture and forestry ministers also agreed last week to take collective action to minimise and eventually eliminate crop burning.

Is climate change making it worse?
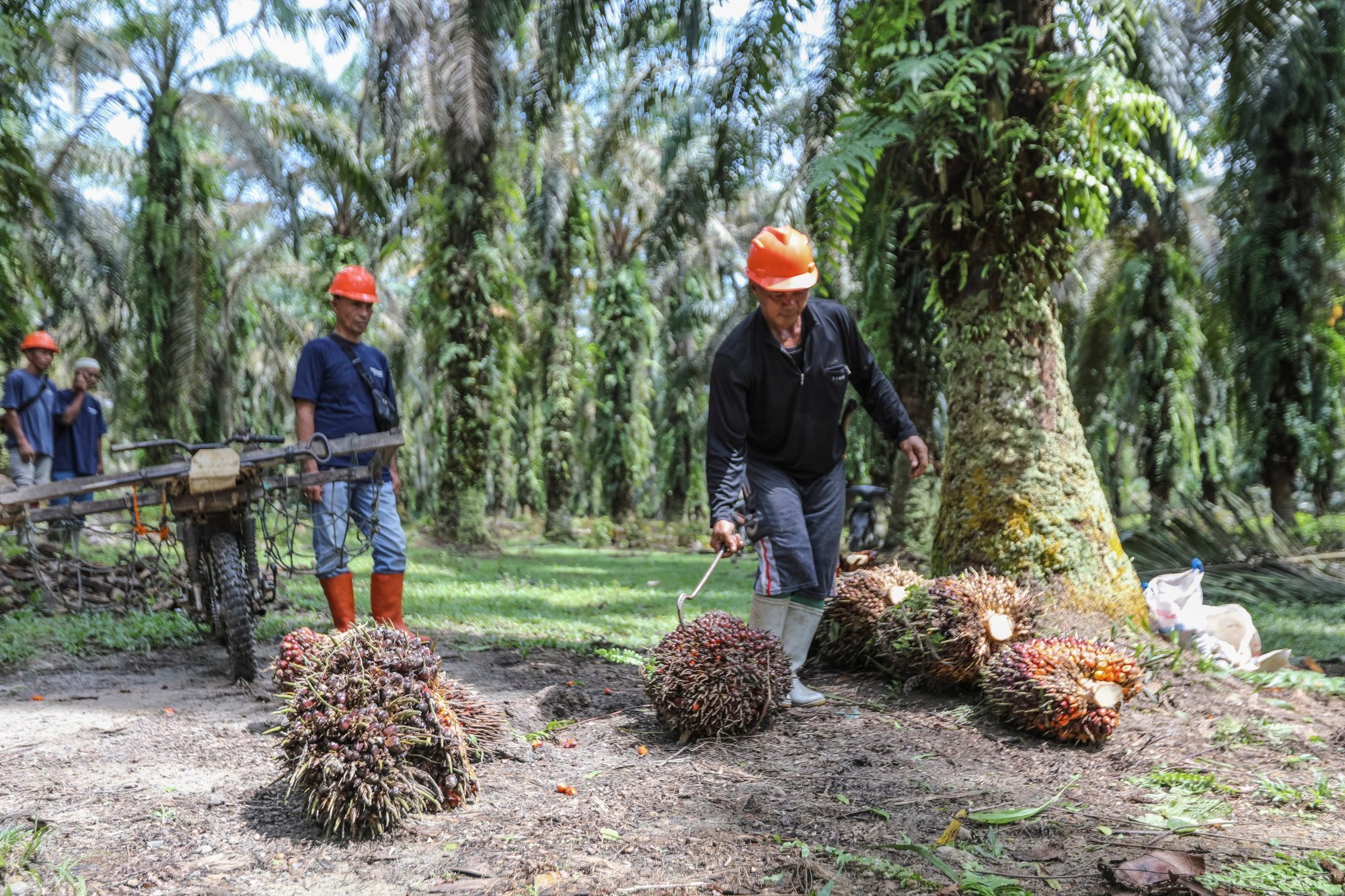
Indonesia is home to the world’s third largest rainforest area and the government needs to take more action, environmentalists say.
The country is experiencing exacerbated dry conditions due to the El Nino weather pattern this year.
Greenpeace Indonesia says climate warming is increasing the intensity and frequency of forest and land fires, which are in turn fuelling the climate crisis.
Malaysia, Indonesia unite to fight ‘discriminatory’ EU over palm oil curbs
Malaysia, Indonesia unite to fight ‘discriminatory’ EU over palm oil curbs
Global consumption of palm oil, used in a wide range of products such as biscuits, candles and cooking oil, is growing rapidly.
Palm oil is the world’s most used edible oil, accounting for 60 per cent of global vegetable oil exports.
For Indonesia, the world’s biggest palm oil producer, the product is one of the biggest export earners after coal. Export earnings from palm oil and its derivatives stood at US$39.28 billion in 2022, according to the Indonesian Palm Oil Association.
[ad_2]
Source link






